
Dr.Mrs.Dhruba Ray
MBBS, DGO(Cal), MD(O&G), FICS
Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician
Uterine Fibroid Treatment in Kolkata, India
+91 91238 89310+91 91431 80185+91 98367 77450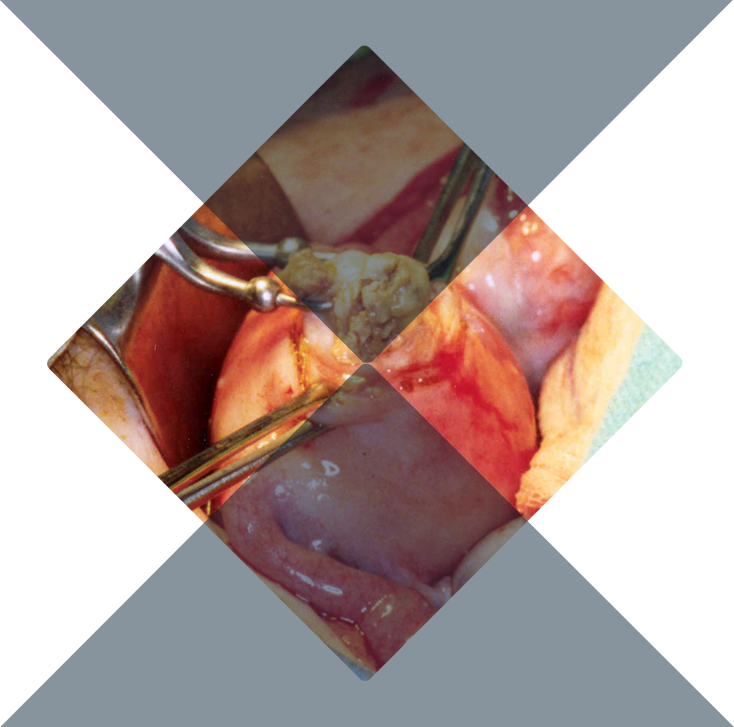


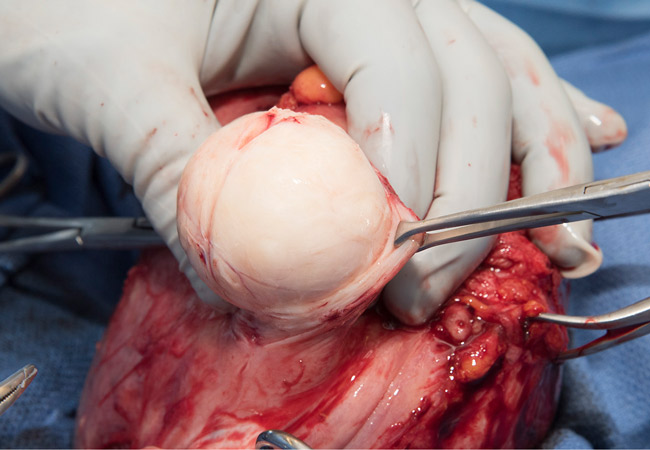
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids, also called uterine leimyomas or myomas, are non-cancerous growths that originate in the muscular wall of the uterus. Fibroids are the most common type of tumor found in female reproductive organs.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids :
Many women with fibroids do not have any symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
Heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding
Painful menstrual periods
Pressure and pain in the abdomen and lower back
Bloated and swollen abdomen
Frequent urination
Constipation
Pain during intercourse
Treatment :
Women without symptoms do not need treatment, but they should be evaluated regularly by their doctors. Women with symptoms from their fibroids have many options for treatment, including drugs and surgery. Several of these treatment options impact a woman's chances of becoming pregnant.
Fibroids usually shrink after menopause, so many women close to menopause (average age 51 to 52) choose to defer treatment. This, however, is a slow process and it should not be assumed that very large fibroids will shrink away quickly after menopause. In a myomectomy, your surgeon removes the fibroids, leaving the uterus in place. If the fibroids are few in number, you and your doctor may opt for a laparoscopic or robotic procedure, which uses slender instruments inserted through small incisions in your abdomen to remove the fibroids from your uterus.
Risk Factors :
Uterine fibroids are the most common tumor found in female reproductive organs.
Age :
Fibroids are most common in women from their 30s through early 50s. (After menopause, fibroids tend to shrink.) About 20% to 40% of women age 35 and older have fibroids of significant enough size to cause symptoms.

A challenging job to cure critical patients.