|
Nephrology is a branch of internal medicine and pediatrics dealing with the study of the function and diseases of the kidney.
Nephrology concerns the diagnosis and treatment of kidney diseases, including electrolyte disturbances and hypertension, and the care of those requiring renal replacement therapy, including dialysis and renal transplant patients.
Many diseases affecting the kidney are systemic disorders not limited to the organ itself, and may require special treatment.
|
| What Is Kidney Disease? |
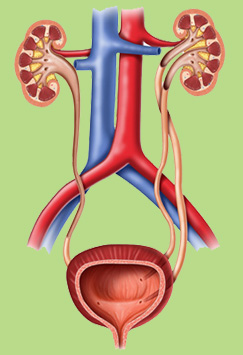
The kidneys are two organs located on either side of your spine in the middle of your back, just above the waist. They perform several life-sustaining roles: They cleanse your blood by removing waste and excess fluid, maintain the balance of salt and minerals in your blood, and help regulate blood pressure.
When the kidneys become damaged, waste products and fluid can build up in the body, causing swelling in your ankles, vomiting, weakness, poor sleep, and shortness of breath. If left untreated, diseased kidneys may eventually stop functioning completely. Loss of kidney function is a serious -- and potentially fatal -- condition.
Each bean-shaped kidney is 4-5 inches long and contains about a million nephrons, which are like tiny pouches. Each nephron has a filter at one end, called a glomerulus, to filter your blood. Your overall kidney function can be measured by how quickly blood is filtered through these glomeruli. This measurement is called the glomerular filtration rate. |
Healthy kidneys handle several specific roles: |
- Maintain a balance of water and concentration of minerals, such as sodium, potassium, and phosphorus, in your blood
- Remove waste by-products from the blood after digestion, muscle activity, and exposure to chemicals or medications
- Produce renin, an enzyme that helps regulate blood pressure
- Produce erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production
- Produce an active form of vitamin D, needed for bone health
|
| What Causes Acute Kidney Injury (Acute Renal Failure)? |
The loss of kidney function is called acute kidney injury, also known as acute renal failure (ARF). This can  occur following a traumatic injury with blood loss, the sudden reduction of blood flow to the kidneys, damage to the kidneys from shock during a severe infection called sepsis, obstruction of urine flow, or damage from certain drugs or toxins. occur following a traumatic injury with blood loss, the sudden reduction of blood flow to the kidneys, damage to the kidneys from shock during a severe infection called sepsis, obstruction of urine flow, or damage from certain drugs or toxins.
Acute kidney injury can also occur from pregnancy complications, such as eclampsia and pre-eclampsia, or related HELLP Syndrome.
Marathon runners and other athletes who don't drink enough fluids while competing in long-distance endurance events may suffer acute renal failure due to a sudden breakdown of muscle tissue. This muscle breakdown releases a chemical called myoglobin that can damage the kidneys.
Obstruction of urine flow, such as with an enlarged prostate, also can lead to acute kidney injury. |
| What Causes Chronic Kidney Disease? |
Kidney damage and decreased function that lasts longer than 3 months is called chronic kidney disease (CKD). Chronic kidney disease is particularly dangerous, because you may not have any symptoms until considerable, often irreparable, kidney damage has been done.
Diabetes (types 1 and 2) and high blood pressure are the most common causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Other causes are:
Immune system conditions, such as lupus, and chronic viral illnesses such as HIV/AIDS, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. |
| Treatment: |
Treatment Choice: Hemodialysis
 Hemodialysis cleans and filters your blood using a machine to temporarily rid your body of harmful wastes,extra salt, and extrawater. Hemodialysis helps control blood pressure and helps your body keep the proper balance of important chemicals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and bicarbonate. Hemodialysis cleans and filters your blood using a machine to temporarily rid your body of harmful wastes,extra salt, and extrawater. Hemodialysis helps control blood pressure and helps your body keep the proper balance of important chemicals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and bicarbonate.
Dialysis can replace part of the function of your kidneys. Diet, medications, and fluid limits are often needed as well. Your diet, fluids, and the number of medications you need will depend on which treatment you choose.
Treatment Choice: Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis is another procedure that removes wastes, chemicals, and extra water from your body. This type of dialysis uses the lining of your abdomen, or belly, to filter your blood. This lining is called the peritoneal membrane and acts as the artificial kidney.
Treatment Choice: Kidney Transplantation
Kidney transplantation surgically places a healthy kidney from another person into your body. The donated kidney does enough of the work that your two failed kidneys used to do to keep you healthy and symptom free.
|
|

