Minimal Invasive Surgery - Laparoscopy
1) Acute Intussusception
In infants, sometimes a portion of the intestine enters into the lumen of an adjacent intestine creating a subacute intestinal obstruction. This is called intussusception. The focus (the portion of the intestine which enters) is called the intussuscipiens and the receiving intestine (which bears the brunt of the damage) is called the intussusceptum.
What is the commonest age at which this occurs?
This usually occurs during the weaning period, i.e 6-8 months, but rarely children of all age groups may present with intussusception. The inflammation of Payer’s patches may occur due to sudden change in dietary pattern of the baby resulting in intussusception. If it occurs in an atypical age, the probability of finding a second pathology should be kept in mind (eg. lymphoma) which serves as the apex of the intussusception.
What are the presenting features?
Usually the baby has a bout of diarrhea, with passage of blood and mucus in stool, which fails to resolve with conservative treatment. Gradually the baby passes blood in stool (red currant jelly stool), and has severe colicky pain. The baby doubles up in bed and cries inconsolably. If neglected the baby may have abdominal distension and bilious vomiting. Interestingly, one or the other of the above mentioned features may be absent.
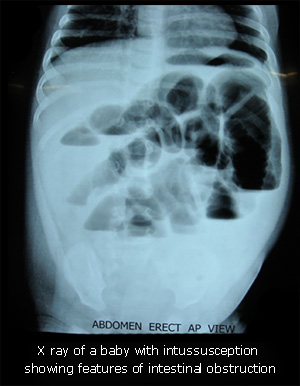
How is the diagnosis confirmed?
The gold standard of diagnosis of intussusception is ultrasonography. But, as we all know, results depend on the expertise of the sinologist. A good sonologist can always pick up intussusception.
How soon should it be treated?
Early diagnosis is the cornerstone of treatment of intussusception. The physician must keep in mind the possibility of this disease entity while treating babies. The sooner it is treated, less are the complications.
Is there no medical treatment available?
Non-operative treatment are feasible if the ailment is diagnosed early.
Options are
• Hydroscopic reduction
• Pneumatic reduction
We prefer hydrostatic reduction of intussusception. Once diagnosed, the baby is taken to the operative room. We need an experienced radiologist trained and experienced in ultrasonography with us. Under ultrasonographic guidance, water is introduced under pressure through the rectum and the reduction of intussusception can be seen and documented. If it fails, surgical treatment is necessary.
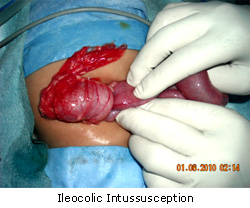
What are the surgical options?
1) Traditionally, these babies underwent opening of the abdomen (laparotomy) and reduction of the intussusception, and in case of loss of vitality of the intestine, resection and end to end anastomosis of the healthy gut segments.
2) Nowadays, with the advent and progress of PEDIATRIC LAPAROSCOPY, the reduction of intussusception can be done without opening the abdomen with laparoscopic guidance.
2) Advantages of Pediatric Laparoscopy
a) The procedure is non-invasive, painless and done easily with fine instruments.
b) The entire procedure isdone under vision and one does not miss a small perforation or leave behind a devitalized intestinal segment, which otherwise may lead to catastrophe and even mortality.
c) Even if intestinal resection is required, the concerned intestinal segment can be brought out through a small incision limiting morbidity of the procedure.
Any long time concerns?
Theoretically, even after correction, such an event may occur again in the lifetime of the baby. But it is extremely unusual. In our experience, we have never seen any recurrence. Possibly, due to the handling of the intestine, some amount of adhesions occur with the surroundings which perhaps prevent further episodes.
Laparoscopic Herniotomy on a 4 years Child with Inguinal Hernia
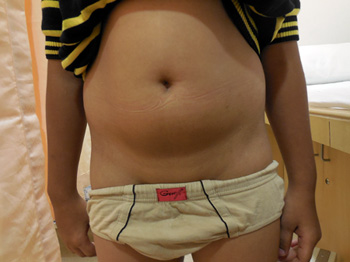
Postoperative picture after Laparoscopic Hernia Repair in a Small Child - it is almost Scarless.