

Dr. Swapan Kumar De
Senior Most Interventional Cardiologist at
Apollo Multispeciality Hospital Kolkata.
MD, DM (Cardiology)
Radiofrequency Ablation Specialist in Kolkata, India




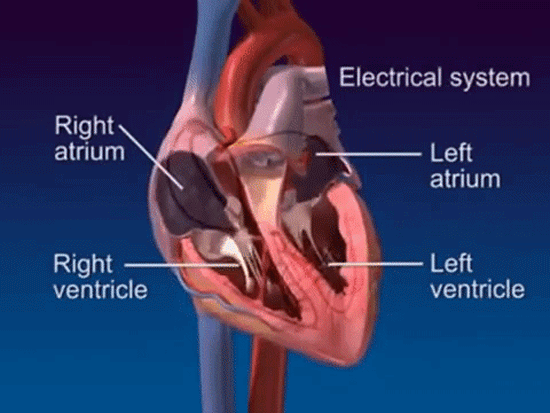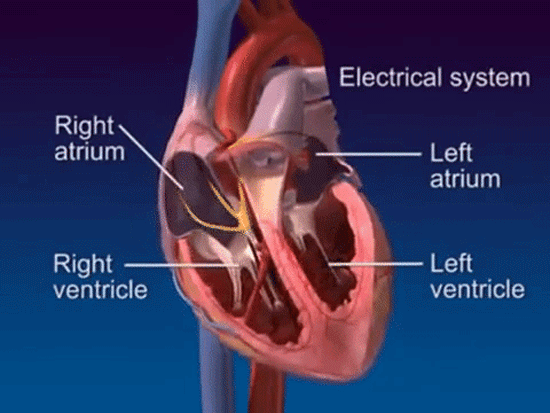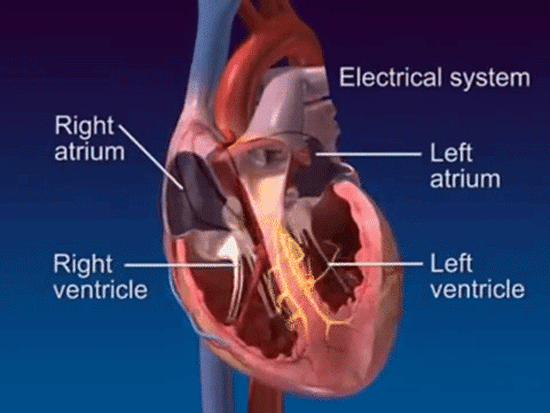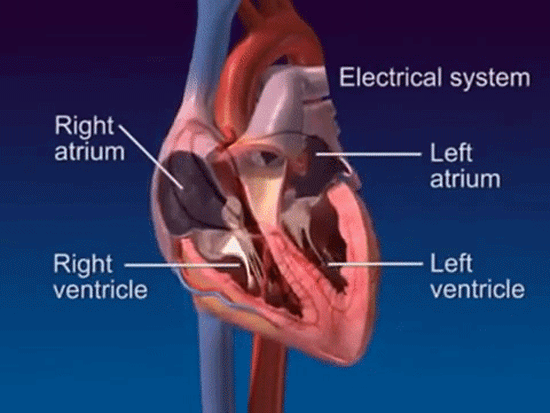
The heart is a muscle that contracts in rhythmic sequence for the duration of our lifetime. Each beat is stimulated by an electrical signal that is generated by the heart's conduction system. A normal heart beats 60 to 100 times per minute.
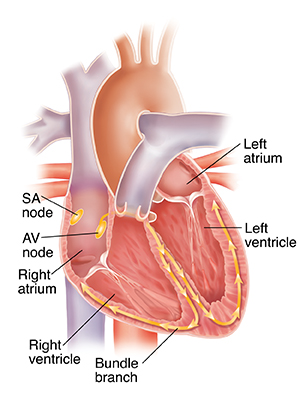
In a normal heartbeat, the heart's electrical signal follows a specific pathway through the heart. The signal begins in the sino-atrial node, or SA node, located in the right atrium. The SA node triggers the atria to contract, pushing blood into the ventricles. The electrical signal then travels through the atrio-ventricular node, or AV node, and into the ventricles. The signal now causes the ventricles to contract, pumping blood into the lungs and body.
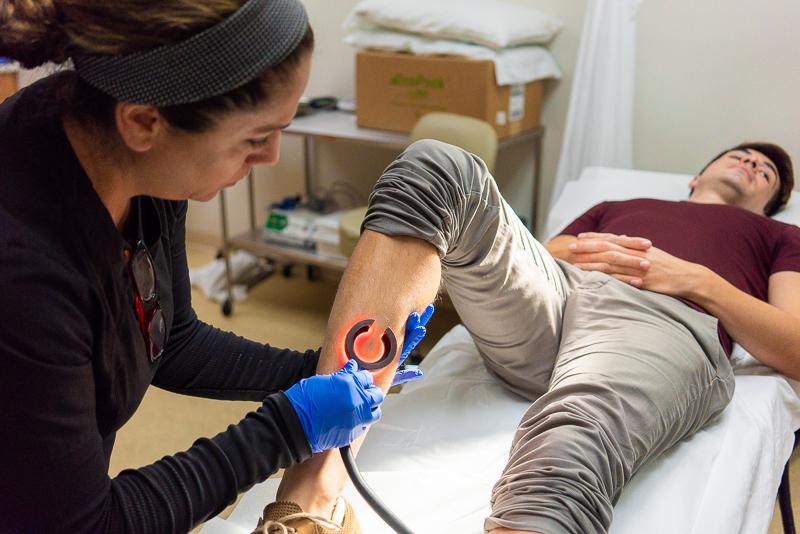
Sometimes, a problem with the conduction system causes the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or to have an erratic or irregular beat. Radiofrequency ablation is a medical procedure used to correct an arrythmia, or irregular heart beat.
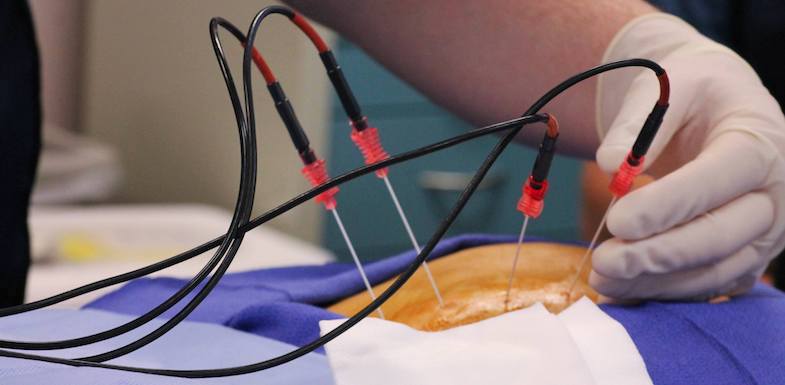
Before ablation, electrophysiology studies will be obtained to identify the exact area of the heart that needs to be treated. During the ablation procedure, a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg, and is guided through the artery and into the heart. Once the catheter reaches the target site in the heart, electrodes at the tip of the catheter emit radio energy.
This energy will heat and destroy the heart tissue causing the abnormal rhythm. In most cases, the heart returns to a normal rhythm following ablation. However, some patients may still require medication or pacemaker insertion.
There are several potential complications associated with this procedure that should be discussed with a doctor prior to surgery.
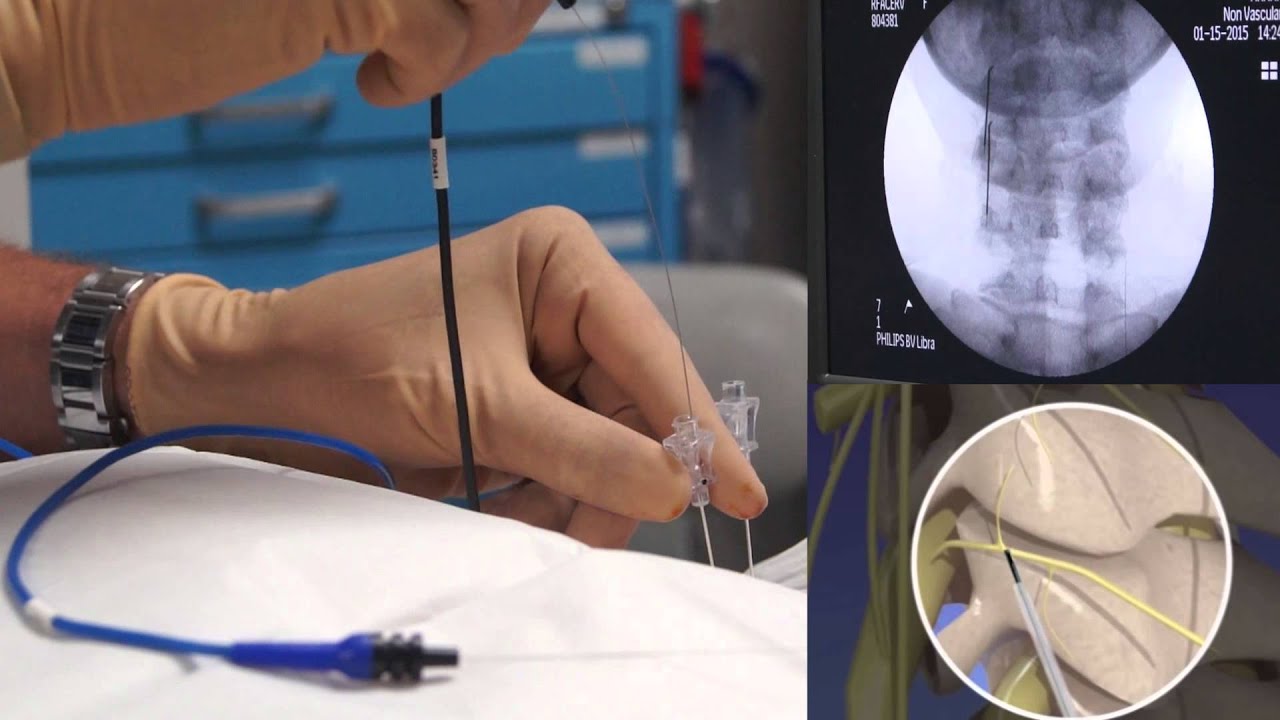
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) may be right for you if have: Pain relief following a nerve block injection. This tells your provider that that particular nerve is the source of your pain and is an appropriate target for RFA.
About Cardiologists : Cardiologists treat people with diseases or conditions of the heart and people who want to learn the risk factors for heart disease. A primary care doctor or family practice doctor can work with a cardiology specialist to diagnose, treat, and manage heart conditions and help people make heart-healthy lifestyle choices. Patients who are at risk for heart disease or have a history of heart symptoms may see a clinical cardiologist regularly. People with ongoing heart conditions, pacemakers, or frequent heart trouble are likely to see a cardiologist with a subspecialty.