Ovulation Induction:
Ovulation induction is the stimulation of ovulation by medication. Strictly, ovulation induction would specifically refer only to the induced ovulation of already mature follicles in the ovaries. However, the term is usually used for stimulation of the development of ovarian follicles to reverse anovulation or oligoovulation. In any case, ovarian stimulation (in the sense of stimulating the development of oocytes) is often used in conjunction with ("strict") ovulation induction.Also, a few definitions also include ovarian hyperstimulation (stimulating the development of multiple follicles of the ovaries in one single cycle) in the definition of ovarian stimulation. Otherwise, ovarian hyperstimulation may still be a side effect of ovulation induction.
IUI (Intra Uterine Insemination):
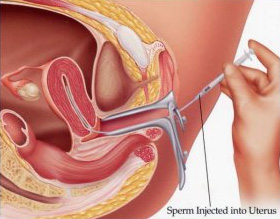 This procedure relies on the natural ability of sperm to fertilize an egg within the reproductive tract. It is useful in cases where infertility is caused by Cervical Mucus Incompatibility, Elevated ASA, Low Sperm Survival, High Seminal Viscosity, Poor Sperm Morphology, Unexplained Infertility, Impotence or Premature Ejaculation. This procedure relies on the natural ability of sperm to fertilize an egg within the reproductive tract. It is useful in cases where infertility is caused by Cervical Mucus Incompatibility, Elevated ASA, Low Sperm Survival, High Seminal Viscosity, Poor Sperm Morphology, Unexplained Infertility, Impotence or Premature Ejaculation.
The aim is to introduce a quantity of sperm into the uterus in order to encourage fertilization. The procedure is simple. We induce ovulation in the female partner by fertility drugs. Then place a prepared semen sample high in the uterus through a fine catheter. It is important here that at least one of the fallopian tubes of the female partner is open.
Step by Step in IUI:
- Drug Treatment to encourage 2 or 3 eggs to mature
-- Usually gonadotrophins to stimulate the growth of the follicles & cause ovulation.
-- When the largest follicle has reached a diameter of around 18mm, a final injection (of hCG) is givn; IUI is usually performed 38 hours later.
- Throughout the drug phase, treatment is monitored, to measure the growth of follicles, individualise drug doses & prevent serious side effects
-- By transvaginal untrasoun dscanning (2 or 3 times during a treatment cycle)
-- Sometimes by measuring hormones in a blood sample
- Sperm, either provided on the morning of ovulation or from a frozen sample, is prepared (washed) & inserted later that day directly into the uterus
- Pregnancy testing, monitoring
IVF (In-Vitro Fertilization):
This is the test tube method, more correctly known as in vitro (in glass) fertilization (IVF). Fertilization takes place outside the woman's body. Most clinics suppress the action of the woman's own LH and FSH by using an injection or a nasal spray (down-regulation). The ovaries are then stimulated with daily injections in the same way as ovulation induction with gonadotrophins (see above).
Monitoring is again by ultrasound and blood tests. Once there are sufficient follicles of the correct size, an injection of HCG is given. The eggs are removed from the ovary 36 to 40 hours later. This is done using a fine needle placed into the vagina and is performed under sedation. The eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory.
After a few days, when fertilization is confirmed, the fertilized egg (embryo) is returned to the womb. The chance of a positive pregnancy test after a fresh cycle of IVF varies, but is approximately 20 to 30 per cent. To maximize the chances of a pregnancy, two embryos are usually returned at the same time, which is why there is an increased chance of twin pregnancies.
If sufficient embryos of good quality develop there may be an option to freeze them and replace them, after thawing, in a subsequent cycle. The success of a frozen embryo transfer is slightly less than that of a fresh cycle.
The availability of IVF on the National Health Service varies considerably from one part of the country to the other. Couples often have to be prepared to pay to have their treatment at a private hospital.
Step by Step in IVF:
- Drug Treatment to stimulate several eggs to mature
-- GnRH agonists to suppress all other hormone activity (injections/nasal spray for usually 2 weeks before gonadotropins & then a further 10-14 days depending on response); a new type of injection drug, known as GnRH antagonist, will reduce this treatment phase by more than a week
-- Gonadotropins to stimulate he growth of follicles & cause ovulation
- Monitoring of treatment, to measure the growth of follicles, individualise drug doses & prevent serious side effects
-- By transvaginal untrasoun dscanning (2 or 3 times during a treatment cycle)
-- Sometimes by measuring hormones in a blood sample
- Egg collection, usually under local anaesthetic, lasts between 10 & 20 minutes
-- Guided by transvaginal untrasound
-- Collected thtough vagina (32-36 hours after final hormone injection)
- Sperm sample, provided on the same day as egg collection
- Fertilisation
-- Eggs & sperm prepared & prepared & cultured together overnight
-- Eggs examined next day under microscope
- Embryo transfer (usually 2 or 3 days after fertilisation)
-- Transvaginal transfer of no more than 3 embryos (usually 2)
-- Embryos placed in the womb
-- Good quality spare embryos usually frozen
- Pregnancy testing, monitoring
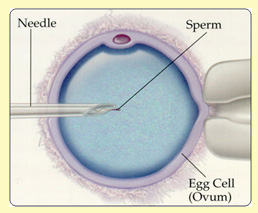 ICSI (Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection): ICSI (Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection):
This is a technique used for male infertility, or for those patients where poor or no fertilization has been achieved after a cycle of IVF. The procedure is very similar to IVF. However, with ICSI a single sperm is injected into a single egg in the laboratory. The success rates are similar to those with IVF.
Normally sperm is obtained by masturbation. Under certain circumstances sperm may be obtained directly from the testis by a minor operation.
Step by Step in ICSI:
- Drug Treatment to stimulate several eggs to mature
-- GnRH agonists to suppress all other hormone activity (injections/nasal spray for usually 2 weeks before gonadotropins & then a further 10-14 days depending on response); a new type of injection drug, known as GnRH antagonist, will reduce this treatment phase by more than a week
-- Gonadotropins to stimulate he growth of follicles & cause ovulation
- Monitoring of treatment, to measure the growth of follicles, individualise drug doses & prevent serious side effects
-- By transvaginal untrasoun dscanning (2 or 3 times during a treatment cycle)
-- Sometimes by measuring hormones in a blood sample
- Egg collection, usually under local anaesthetic, lasts between 10 & 20 minutes
-- Guided by transvaginal untrasound
-- Collected thtough vagina (32-36 hours after final hormone injection)
- Sperm sample, provided on the same day as egg collection.The sample can be obtained in a natural way or following aspirations from the spididymis (PESA/MESA) or extraction frok the testis (TESE)
- Fertilisation
-- One sperm cell is injected into a single eggt
-- Eggs examined next day under microscope to see whether fertilisation has occured
- Embryo transfer (usually 2 or 3 days after fertilisation)
-- Transvaginal transfer of no more than 3 embryos (usually 2)
-- Embryos placed in the womb
-- Good quality spare embryos usually frozen
- Pregnancy testing, monitoring
Egg Donation & Egg Sharing:
It is considered for women who is a poor responder to the ovulation induction drugs, has reduced ovarian reserve, or is a carrier of a genetic condition. All the steps are IVF are performed except the egg donor undergoes the ovulation induction and egg retrieval. Once the eggs are retrieved , they are fertilized with the partner’s sperms. Legal, medical and Psycho logic counseling are required.
Step by Step in Egg Donation:
- Drug Treatment to stimulate several eggs to mature
-- GnRH agonists to suppress all other hormone activity (injections/nasal spray for usually 2 weeks before gonadotropins & then a further 10-14 days depending on response); a new type of injection drug, known as GnRH antagonist, will reduce this treatment phase by more than a week
-- Gonadotropins to stimulate he growth of follicles & cause ovulation
- Monitoring of treatment, to measure the growth of follicles, individualise drug doses & prevent serious side effects
-- By transvaginal untrasoun dscanning (2 or 3 times during a treatment cycle)
-- Sometimes by measuring hormones in a blood sample
- Egg collection, usually under local anaesthetic, lasts between 10 & 20 minutes
-- Guided by transvaginal untrasound
-- Collected thtough vagina (32-36 hours after final hormone injection)
- IVF with sperm of recepient's male partner
PESA/TESA:
PESA (Percutaneous Epidydimal Sperm Aspiration) and TESA (Testicular Sperm Aspiration) procedure should be used when there is no sperm in ejaculate (so called ‘azoospermia) confirmed in two independent semen assessments.
The procedure can be done under local anaesthesia or short intravenous sedation. For aspiration of sperm from the epidydymis (so called PESA) as well as for aspiration of sperm directly from the testicles (so called TESA) we use special, fine needles which make the procedure less invasive.
PESA/TESA takes about 15-20 minutes and sperm aspirated during that procedure are usually cyropreserved and are to be used for ICSI (IVF with injection of a single, selected sperm) on the day of the egg collection.
|