Dr. Biplab Dolui
MS (Orthopaedics), AFTS Fellow (Paris), Consultant Arthroscopist, Joint Replacement & Trauma Surgeon
MS (Orthopaedics), AFTS Fellow (Paris), Consultant Arthroscopist, Joint Replacement & Trauma Surgeon
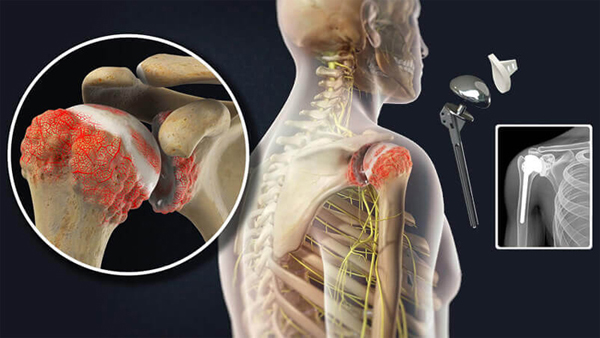
Shoulder replacement is a surgical procedure in which all or part of the glenohumeral joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant. Such joint replacement surgery generally is conducted to relieve arthritis pain or fix severe physical joint damage.
Shoulder replacement surgery is an option for treatment of severe arthritis of the shoulder joint. Arthritis is a condition that affects the cartilage of the joints. As the cartilage lining wears away, the protective lining between the bones is lost. When this happens, painful bone-on-bone arthritis develops. Severe shoulder arthritis is quite painful, and can cause restriction of motion. While this may be tolerated with some medications and lifestyle adjustments, there may come a time when surgical treatment is necessary.
There are a few major approaches to access the shoulder joint. The first is the deltopectoral approach, which saves the deltoid, but requires the subscapularis to be cut. The second is the transdeltoid approach, which provides a straight on approach at the glenoid. However, during this approach the deltoid is put at risk for potential damage.
When to contact your surgeon
• Fever above 38 degrees Celsius.
• Increased pain unrelieved with pain medications.
• Sudden, severe shoulder pain.
• Increased redness around the incision.
• Increased swelling at the incision.
• A bulge that can be felt at the shoulder.
• Shoulder pain, tenderness or swelling.
• Numbness or tingling in the arm.
• Change in arm length.
• Change in colour and temperature of the arm.
• Change in motion ability.
• Drainage or odour from the incision.
• Any sign of any infection anywhere in your body should be reported to your GP as soon as possible and most likely you will need to start antibiotics.