|
||||||||||||||
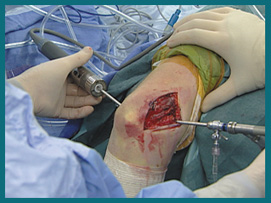 What is arthroscopic surgery?
What is arthroscopic surgery?Arthroscopic surgery is one of the most common orthopedic procedures performed today. Through the use of small instruments and cameras, an orthoapedic surgeon can visualize, diagnose, and treat problems within the joints.
One or more small incisions are made around the joint to be viewed. The surgeon inserts an instrument called an arthoscope into the joint. The arthoscope contains a fiber optic light source and small television camera that allows the surgeon to view the joint on a television monitor and diagnose the problem, determine the extent of injury, and make any necessary repairs. Other instruments may be inserted to help view or repair the tissues inside the joint.
What is joint replacement surgery?Joint replacement surgery is performed to replace an arthritic or damaged joint with a new, artificial joint called a prosthesis. The knee and hip are the most commonly replaced joints, although shoulders, elbows and ankles can also be replaced.
Joints contain cartilage, a rubbery material that cushions the ends of bones and facilitates movement. Over time, or if the joint has been injured, the cartilage wears away and the bones of the joint start rubbing together. As bones rub together, bone spurs may form and the joint becomes stiff and painful. Most people have joint replacement surgery when they can no longer control the pain in their hip or knee with medication and other treatments, and the pain is significantly interfering with their lives.
How long do artificial joints last?
On average, artificial joints have a lifespan of 10 to 20 years. If you are in your 40s or 50s when you have joint replacement surgery, especially if you are very active, you are likely to need another joint replacement surgery later in life.
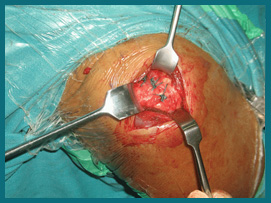 What happens during rotator cuff surgery?
What happens during rotator cuff surgery?Shoulder surgery for rotator cuff problems usually involves one or more of the following procedures: debridement, subacromial decompression, rotator cuff repair.
Debridement clears damaged tissue out of the shoulder joint.
Subacromial decompression involves shaving bone or removing spurs underneath the tip of the shoulder blade (acromion). This creates more room in the space between the end of the shoulder blade and the upper arm bone so that the rotator cuff tendon is not pinched and can glide smoothly.If the rotator cuff tendon is torn, it is sewn together and reattached to the top of the upper arm bone.
What is an ACL reconstruction?
ACL reconstruction is a surgical procedure that repairs a torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), one of the four ligaments that help stabilize the knee. The ligament is reconstructed using a tendon that is passed through the inside of the knee joint and secured to the upper leg bone (femur) and one of the two lower leg bones (tibia).
The tendon used for reconstruction is called a graft and can come from different sources. It is usually taken from the patient’s own patella, hamstring, or quadriceps, or it can come from a cadaver. ACL reconstruction is most often performed through arthroscopic surgery.
What is the difference between a sprain and a strain?
A strain occurs when a muscle or tendon is stretched or torn. A sprain occurs when a ligament is stretched or torn.
Strains are often the result of overuse or improper use of a muscle, while sprains typically occur when a joint is subjected to excessive force or unnatural movements (e.g., sudden twists, turns, or stops). Sprains can be categorized by degree of severity:- A first-degree sprain stretches the ligament but does not tear it. Symptoms include mild pain with normal movement.
- A second-degree sprain is characterized by a partially torn ligament, significant pain and swelling, restricted movement, and mild to moderate joint instability.
- In a third-degree sprain, the ligament is completely torn with mild to severe pain, swelling, and significant joint instability.
What is spinal stenosis?
Stenosis refers to a narrowing of the spinal canal, usually in the lower back (lumbar) region. This narrowing is often a result of the normal degenerative aging process. It occurs as the disks of cartilage that separate the spine’s vertebrae lose water and the space between the vertebrae become smaller, causing friction between the bones. The loss of water in the disks makes them less flexible and unable to act as shock absorbers in the spine. Daily wear and tear on the spine becomes more significant without these shock absorbers.
As the disks degenerate, vertebrae may shift, causing the spinal canal to narrow. In some cases, the nerves that travel through the spinal column to the legs become squeezed. This can cause back and leg pain, and even leg weakness. Arthritis and falls also contribute to the narrowing of the spinal canal, compressing the nerves and nerve roots and causing pain and discomfort.
 What is degenerative disk disease?
What is degenerative disk disease?
Degenerative disk disease is a general term applied to back pain that has lasted for more than three months. It is caused by degenerative changes in the intervertebral disks in the spine and can occur anywhere in the spine: low back (lumbar), mid-back (thoracic), or neck (cervical).
Under the age of 30, these disks are normally soft, and they act as cushions for the vertebrae. With age, the material in these lumbar disks becomes less flexible and the disks begin to erode, losing some of their height. As their thickness decreases, their ability to act as a cushion lessens. The less dense cushion now alters the position of the vertebrae and the ligaments that connect them. In some cases, the loss of density can even cause the vertebra to shift their positions. As the vertebrae shift and affect the other bones, the nerves can get caught or pinched and muscle spasms can occur.
Degenerative disk disease is primarily a result of the normal aging process, but it may also occur as a result of trauma, infection, or direct injury to the disk. Heredity and physical fitness may also play a part in the process.
What is shoulder impingement?
Impingement syndrome is a common disorder of the shoulder that refers to an improper alignment of the bones and tissues in the upper arm. Inflammatory conditions such as tendinitis, bursitis, and arthritis are all closely related to impingement syndrome, as are tears to the rotator cuff tendons.
If the rotator cuff becomes inflamed from overuse or there is a bone deformity or spur on the end of the shoulder blade, then the space between the upper arm bone and tip of the shoulder blade is narrowed, causing the rotator cuff and its fluid-filled bursa to be squeezed or pinched. This impingement causes irritation and pain to the rotator cuff when the shoulder is raised.
What is frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) is a condition in which the tissues around the shoulder joint stiffen, scar tissue forms, andshoulder movements become difficult and painful. It can develop when you stop using the joint normally because of pain, other injury, or a chronic health condition, such as diabetes. Any shoulder problem can lead to frozen shoulder if you do not work to maintain its full range of motion.
 What is a separated shoulder?
What is a separated shoulder?
A shoulder separation (acromioclavicular joint injury) occurs when the outer end of the collarbone separates from the end of the shoulder blade because of torn ligaments. This injury occurs most often from a blow to the shoulder or a fall on a shoulder or outstretched hand or arm.
What is a dislocated shoulder?
A shoulder dislocation (shoulder instability) occurs when the upper end of the arm bone ball pops out of the shoulder joint socket. This injury may be caused by a direct blow to the shoulder, a fall on an outstretched hand or arm, or an exaggerated overhead throwing motion.
What are shin splints?
Shin splints are an inflammation of the periosteum, a fibrous sheath that surrounds bone. In this case, the affected bone is the shin bone, or tibia. Shin splints are usually accompanied by pain and swelling in the front of the lower leg. Most frequent in runners, this overuse injury is caused by the repetitive stress of running on hard surfaces.
 What is bursitis?
What is bursitis?Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa or bursae (more than one bursa), small fluid-filled sacs that cushion areas of friction around joints. Bursae contain synovial fluid that lubricates the joints. Bursitis typically occurs as a result of overuse during physical activities or infection of the synovial fluid. If a bursa becomes infected or irritated from repetitive stress, it will cause pain and limited movement. Bursitis is most common in the shoulder, knee, hip, elbow, or heel.
What is arthritis?
The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, can affect any joint in the body, but most often afflicts the knees, hips, and fingers. Most people will develop osteoarthritis from the normal wear and tear on the joints through the years. Joints contain cartilage, a rubbery material that cushions the ends of bones and facilitates movement. Over time, or if the joint has been injured, the cartilage wears away and the bones of the joint start rubbing together. As bones rub together, bone spurs may form and the joint becomes stiff after long periods of activity or inactivity.
Home I About Doctor I About Orthopeadic I Surgical Videos I Appointment I FAQ I Publication I Award & Certificates Chamber Details I Treatment I Photogallery I Contact Details I Write Your Queries Site Powered By : www.calcuttayellowpages.com |