| |
| Ovarian Cyst |
| |
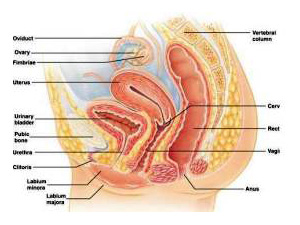
What is the ovary and what are ovarian cysts?
The ovary is one of a pair of reproductive glands in women that are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. The ovaries produce eggs (ova) and female hormones. The ovaries are the main source of female hormones, which control the development of female body characteristics such as the breasts, body shape, and body hair. They also regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Ovarian cysts are closed, sac-like structures within an ovary that contain a liquid, gaseous, or semisolid substance. The ovary is also referred to as the female gonad. |
| |
 |
What causes ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts form for numerous reasons. The most common type is a follicular cyst, which results from the growth of a follicle. A follicle is the normal fluid-filled sac that contains an egg. Follicular cysts form when the follicle grows larger than normal during the menstrual cycle and does not open to release the egg. Usually, follicular cysts resolve spontaneously over the course of days to months. Cysts can contain blood (hemorrhagic cysts) from injury or leakage of tiny blood vessels into the egg sac.
Another type of ovarian cyst that is related to the menstrual cycle is a corpusluteum cyst. The corpus luteum is an area of tissue within the ovary that occurs after an egg has been released from a follicle. If a pregnancy doesn't occur, the corpus luteum usually breaks down and disappears. It may, however, fill with fluid or blood and persist as a cyst on the ovary. Usually, this cyst is found on only one side and produces no symptoms. |
Occasionally, the tissues of the ovary develop abnormally to form other body tissues such as hair or teeth. Cysts with these abnormal tissues are called benign cystic teratomas or dermoid cysts.
Endometriosis is a condition in which cells that normally grow inside the uterus (womb), instead grow outside of the uterus. The ovary is a common site for endometriosis. When endometriosis involves the ovary, the area of endometrial tissue may grow and bleed over time, forming a brown-colored cystic area sometimes referred to as a chocolate cyst or endometrioma.
Both benign and malignant tumors of the ovary may also contain cysts. Furthermore, the condition known as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts within both ovaries. PCOS is associated with a number of hormonal problems and is the most common cause of infertility in women.
Infections of the pelvic organs can involve the ovaries and Fallopian tubes. In severe cases, pus-filled cystic spaces may be present on or around the ovary or tubes. These are known as tubo-ovarian abscesses.
What symptoms are caused by ovarian cysts?
Most ovarian cysts are never noticed and resolve without women ever realizing that they are there. When a cyst causes symptoms, painin the belly or pelvis is by far the most common one. The pain can be caused from :
|
| |
- rupture of the cyst,
- rapid growth and stretching,
- bleeding into the cyst, or
- twisting of the cyst around its blood supply (known as torsion).
|
| |
|
If the cyst has reached a large size, other symptoms may arise as a result of pressure or distortion of adjacent anatomical structures. These symptoms can include abdominal fullness or bloating, indigestion, feeling full after eating only a small amount (early satiety), feeling an urge to defecate or having difficult bowel movements, or pain with sexual intercourse.
How are ovarian cysts diagnosed?
Sometimes ovarian cysts may be noticed by a health care practitioner during a bimanual examination of the pelvis. If a cyst is suspected based upon the symptoms of physical examination, imaging techniques are used. Most cysts are diagnosed by ultrasound, which is the best imaging technique for detecting ovarian cysts. Ultrasound is an imaging method that uses sound waves to produce an image of structures within the body. Ultrasound imaging is painless and causes no harm.
Cysts can also be detected with other imaging methods, such as CT scan or MRI scan (magnetic resonance imaging). |
| |
|
|