 |
 |
 |
| |
| Haematology & Oncology |
| |
Hematology, also spelled haematology , is the study of blood, the blood-forming organs, and blood diseases. Hematology includes the study of etiology, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and prevention of blood diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, and the mechanism of coagulation. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
| Leukaemia |
| |
In people with Leukaemia, the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells, called Leukaemia cells. At first, Leukaemia cells function almost normally. But over time, as more Leukaemia cells are produced, they may crowd out the healthy white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. This makes it difficult for the blood to carry out its normal functions. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
| Lymphoma |
| |
Any of a large group of cancers of lymphocytes (white blood cells). Non-Hodgkin lymphomas can occur at any age and are often marked by lymph nodes that are larger than normal, fever, and weight loss. There are many different types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These types can be divided into aggressive (fast-growing) and indolent (slow-growing) types, and they can be formed from either B-cells or T-cells. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
| |
| Myeloma |
| |
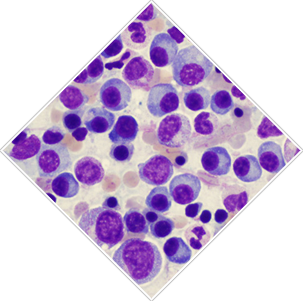
Myeloma begins when a plasma cell becomes abnormal. The abnormal cell divides to make copies of itself. The new cells divide again and again, making more and more abnormal cells. These abnormal plasma cells are called myeloma cells.In time, myeloma cells collect in the bone marrow. They may damage the solid part of the bone. When myeloma cells collect in several of your bones, the disease is called "multiple myeloma." This disease may also harm other tissues and organs, such as the kidneys. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
| Chemotherapy |
| |
Healthy marrow and blood cells are needed to live. Disease can affect the marrow’s ability to function. When this happens a bone marrow or cord blood transplant could be the best treatment option. For some diseases, transplant offers the only potential cure.A bone marrow or cord blood transplant replaces unhealthy blood-forming cells with healthy ones. Blood-forming cells are also called blood stem cells. Blood stem cells are immature cells that can grow into red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
| Bone Marrow Transplantation |
| |
The word chemotherapy simply means drug treatment. The aim of chemotherapy is to selectively damage and kill cancer cells. There are many different chemotherapy drugs which work in different ways. You may receive one or more drugs as part of your treatment. Chemotherapy can be given in a number of ways. Oral (by mouth): You may be given capsules or tablets to take. If you have any trouble swallowing the tablets whole, you should inform your doctor or nurse. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
| |
| Anaemias |
| |
Anemia is a condition that develops when your blood does not contain enough healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin. These cells are important for carrying oxygen around the body. Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia in India and worldwide. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
| Thalassemia |
| |
Thalassemia major occurs when a child inherits two mutated genes, one from each parent. Children born with thalassemia major usually develop the symptoms of severe anemia within the first year of life. They lack the ability to produce normal, adult hemoglobin and experience chronic fatigue. They may also fail to thrive. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
| Haemophilia |
| |
Haemophilia is a condition that stops a person's blood clotting normally. Haemophilia is usually inherited and passed on to a child by one or both parents. More boys than girls are affected. A person with haemophilia has a lower amount of clotting factors in the blood. |
| |
| view more |
|
| |
|
|
 |
| |
| Platelet Disorders |
| |
• Severe disorders of platelet function: Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS), Glanzmann's thrombasthenia (GT), Bernard-Soulier syndrome (BSS).
• Disorders of receptors and signal transduction: platelet cyclo-oxygenase deficiency, thromboxane synthase deficiency, thromboxane A2 receptor defect, ADP receptor defect. |
| |
| view more |
|
 |
| |
| Other Blood Disorders |
| |
Anemia of chronic disease: People with chronic kidney disease or other chronic diseases tend to develop anemia. Anemia of chronic disease does not usually require treatment. Injections of a synthetic hormone (Epogen, Procrit) to stimulate the production of blood cells or blood transfusions may be necessary in some people with this form of anemia. |
| |
| view more |
|
|