|
Hemophilia Facts
• Hemophilia is one of a group of inherited bleeding disorders that cause abnormal or exaggerated bleeding and poor blood clotting.
• Hemophilia A and B are inherited in an X-linked recessive genetic pattern, so males are commonly affected while females are usually carriers of the disease.
• Hemophilia A is caused by a deficiency of clotting Factor VIII, while hemophilia B (also called Christmas disease) results from a deficiency of Factor IX.
• Hemophilia varies in its severity among affected individuals.
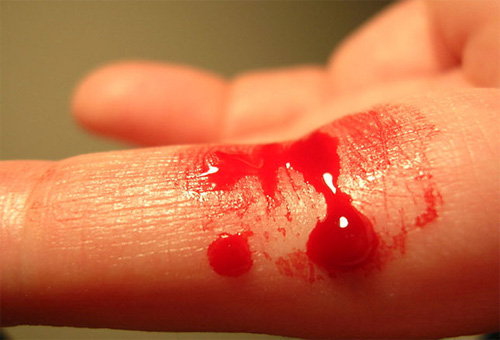
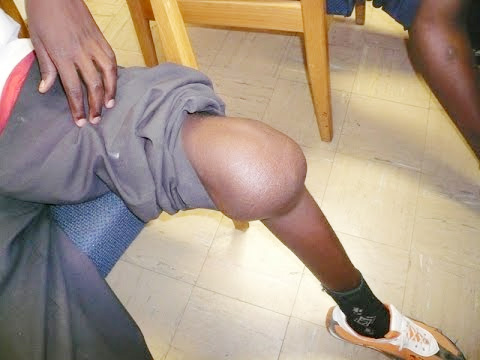
• Symptoms include excessive bleeding from any site in the body; long-term damage to joints from repeated bleeding episodes is characteristic.
• Treatment involves coagulation factor replacement therapy.
• The formation of inhibitors to the treatment factor concentrates is a significant complication of treatment.
• Gene therapy treatments are a source of active research and hold promise for the future.z
What is hemophilia?
Hemophilia is not one disease but rather one of a group of inherited bleeding disorders that cause abnormal or exaggerated bleeding and poor blood clotting. The term is most commonly used to refer to two specific conditions known as hemophilia A and hemophilia B, which will be the main subjects of this article. Hemophilia A and B are distinguished by the specific gene that is mutated (altered to become defective) and codes for a defective clotting factor (protein) in each disease. Rarely, hemophilia C (a deficiency of Factor XI) is encountered, but its effect on clotting is far less pronounced than A or B.
Hemophilia A and B are inherited in an X-linked recessive genetic pattern and are therefore much more common in males. This pattern of inheritance means that a given gene on the X chromosome expresses itself only when there is no normal gene present. For example, a boy has only one X chromosome, so a boy with hemophilia has the defective gene on his sole X chromosome (and so is said to be hemizygous for hemophilia). Hemophilia is the most common X-linked genetic disease..
 Although it is much rarer, a girl can have hemophilia, but she would have to have the defective gene on both of her X chromosomes or have one hemophilia gene plus a lost or defective copy of the second X chromosome that should be carrying the normal genes. If a girl has one copy of the defective gene on one of her X chromosomes and a normal second X chromosome, she does not have hemophilia but is said to be heterozygous for hemophilia (a carrier). Her male children have a 50% chance of inheriting the one mutated X gene and thus have a 50% chance of inheriting hemophilia from their carrier mother..
Although it is much rarer, a girl can have hemophilia, but she would have to have the defective gene on both of her X chromosomes or have one hemophilia gene plus a lost or defective copy of the second X chromosome that should be carrying the normal genes. If a girl has one copy of the defective gene on one of her X chromosomes and a normal second X chromosome, she does not have hemophilia but is said to be heterozygous for hemophilia (a carrier). Her male children have a 50% chance of inheriting the one mutated X gene and thus have a 50% chance of inheriting hemophilia from their carrier mother..
Hemophilia A occurs in about 1 out of every 5000 live male births. Hemophilia A and B occurs in all racial groups. Hemophilia A is about four times more common than B. B occurs in about 1 out of 20- 30,000 live male births..
Hemophilia has been called the Royal Disease because Queen Victoria, Queen of England from 1837 to 1901, was a carrier. Her daughters passed the mutated gene on to members of the royal families of Germany, Spain, and Russia. Alexandra, Queen Victoria's granddaughter, who became Tsarina of Russia in the early 20th century when she married Tsar Nicholas II, was a carrier. Their son, the Tsarevich Alexei, suffered from hemophilia
|