Dr. Sankar Dasmahapatra
Gynae Laparoscopic Surgeon in Kolkata, India
DGO, MS, Fellowship in Gynaecological Lap Surgery (Sydney -Australia)
Consultant Gynaecologist & Obstetrician
Infertility Specialist & Lapaoscopic Surgeon
DGO, MS, Fellowship in Gynaecological Lap Surgery (Sydney -Australia)
Consultant Gynaecologist & Obstetrician
Infertility Specialist & Lapaoscopic Surgeon
The Following Surgeries are Routinely Performed:
Diagnostic Laparoscopy and Laparoscopic Sterilization
Laparoscopic Management of Ovarian Cyst
Laparoscopic Salpingo-Oophorectomy
Laparoscopic Management of Tubal Pregnancy
Laparoscopic Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy
Laparoscopic Total Hysterectomy
Supracervical Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Laparoscopic Re-canalization Surgery
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
Laparoscopic Burch Suspension
Laparoscopic Myomectomy
Laparoscopic Intestinal and Tubal Anastomosis
Laparoscopic Sacro-Colpopexy
Radical Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Laparoscopic Pelvic Floor Repair
TVT and TOT & TVTO for Stress Urinary Incontinence
Laparoscopic Vesico-Vaginal Fistula Repair
Laparoscopic Lymphadenectomy for Gynecological Malignancies
Laparoscopic uterine nerve ablation (LUNA) for chronic pelvic pain
Laparoscopic Recanalization Surgery
Laparoscopic Fimbrioplasty
Laparoscopic Presacral Neurectomy
Laparoscopic Management of severe Endometriosis
Operative Hysteroscopy (Submucous Myomectomy, Metroplasty & TCRE)
Simple Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic Movie Making and Video Editing
Digital Prescription Writing technique
Colposcopy
Simple da Vinci Robotic Surgery
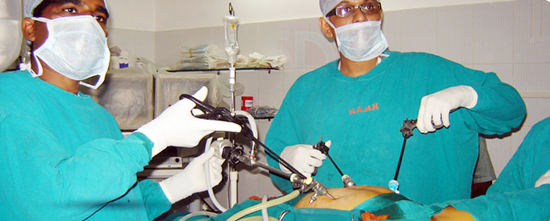
Laparoscopic Surgery - What Is It?
Laparoscopic or “minimally invasive” surgery is a specialized technique for performing surgery. In the past, this technique was commonly used for gynecologic surgery and for gall bladder surgery. Over the last 10 years the use of this technique has expanded into intestinal surgery. In traditional “open” surgery the surgeon uses a single incision to enter into the abdomen. Laparoscopic surgery uses several 0.5-1cm incisions. Each incision is called a “port.” At each port a tubular instrument known as a trochar is inserted. Specialized instruments and a special camera known as a laparoscope are passed through the trochars during the procedure. At the beginning of the procedure, the abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to provide a working and viewing space for the surgeon. The laparoscope transmits images from the abdominal cavity to high-resolution video monitors in the operating room. During the operation the surgeon watches detailed images of the abdomen on the monitor. This system allows the surgeon to perform the same operations as traditional surgery but with smaller incisions.
In certain situations a surgeon may choose to use a special type of port that is large enough to insert a hand. When a hand port is used the surgical technique is called “hand assisted” laparoscopy. The incision required for the hand port is larger than the other laparoscopic incisions, but is usually smaller than the incision required for traditional surgery.
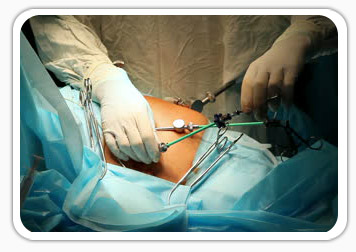
What are the advantages of laparoscopic surgery?
Compared to traditional open surgery, patients often experience less pain, a shorter recovery, and less scarring with laparoscopic surgery.
What kinds of operations can be performed using laparoscopic surgery?
Most intestinal surgeries can be performed using the laparoscopic technique. These include surgery for Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, cancer, rectal prolapse and severe constipation.
In the past there had been concern raised about the safety of laparoscopic surgery for cancer operations. Recently several studies involving hundreds of patients have shown that laparoscopic surgery is safe for certain colorectal cancers.
How safe is laparoscopic surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is as safe as traditional open surgery. At the beginning of a laparoscopic operation the laparoscope is inserted through a small incision near the belly button (umbilicus). The surgeon initially inspects the abdomen to determine whether laparoscopic surgery may be safely performed. If there is a large amount of inflammation or if the surgeon encounters other factors that prevent a clear view of the structures the surgeon may need to make a larger incision in order to complete the operation safely.
Any intestinal surgery is associated with certain risks such as complications related anesthesia and bleeding or infectious complications. The risk of any operation is determined in part by the nature of the specific operation. An individual’s general heath and other medical conditions are also factors that affect the risk of any operation. You should discuss with your surgeon your individual risk for any operation
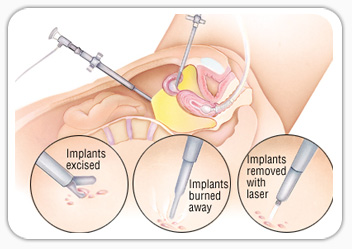
Laparoscopic tubal ligation is one of the most common and effective way of birth control but at times patients want to reverse the process – in medical language it is called laparoscopic tubal recanalization surgery. After successful recanalization patients can try for conception from next menstrual cycle. Fertility outcomes are favourable.
As per our processes we study patient’s case thoroughly, both medical and demographically and we discourage patients under the age of 30 years to go through permanent birth control measures.
Background -
Infertility is defined as a disease characterized by the failure to establish a clinical pregnancy after 12 months of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse in a woman under age 35, or after 6 months in a woman over the age of 35 .Infertility is a common problem throughout the world. It is estimated that more than 186 million people suffer from infertility, the majority being residents of developing countries. Infertility may be primary or secondary. Primary infertility is defined as a woman who has never had a clinical pregnancy. Secondary infertility is the inability to establish a clinical pregnancy but the woman has previously been diagnosed with a. clinical pregnancy. There are both male and female causes for infertility with the most common causes of female infertility being ovulatory dysfunction and tubal disease. Tubal infertility is estimated to account for between 11 and 67% of infertility diagnoses. Tubal infertility can be caused by internal blockage of the fallopian tubes, abnormalities of the internal tube from inflammation or infection, or pelvic adhesions which prevents normal functioning of the fallopian tubes. The blockage of the fallopian tubes may be proximal, in which case, the blockage is commonly composed of debris which forms a plug in the proximal tube. If the blockage is more distal, then the cause is usually previous infection, which may present as a hydrosalpinx with dilatation of the fallopian tube, and no spill from the tube on hysterosalpingogram (HSG). If the fallopian tube is blocked proximally, then selective recanalization of the tubes may be effective in opening the fallopian tube allowing for potential fertility.

What is laparoscopic tubal Recanalization?
The procedure aims at reconnecting the previously cut portions of the fallopian tube. After family planning some women want to reverse the procedure, which created a break in the fallopian tube. The reverse procedure involves reconnecting the fallopian tubes in order to become fertile again.
Laparoscopic tubal recanalization is highly skillful surgery in which fallopian tubes are repaired using very thin suture material (Thread) –As thin as hair of an eyebrow.
We use smaller 3 mm size instruments to conduct the procedure. The segment of the fallopian tube where previous ligation was done is cut so as to get fresh and healthy tube with lumen inside and both the cut ends are sutured together so as to get hollow lumen in continuity with each other.
Advantages Of Laparoscopic Tubal Recanalization Includes
Laparoscopic Tubal recanalization is safe, less painful. Patient recovery is very fast as compared to traditional Tubal recanalization. Patient can be discharged practically on very next day of the surgery.
Laparoscopic tubal recanalization has many advantages over open operation. The principal advantage of laparoscopic tubal recanalization is no big cut is made on the skin, which would result in minimal scarring. The procedure requires only minimal tissue handling, so less postoperative adhesions. The smaller incisions will also aid speedy recovery post surgery. Scope of complications is kept minimal. In most cases, patients will be able to leave the hospital post procedure within hours after having the procedure.
What is the success rate of laparoscopic tubal Recanalization?
Previous studies have reported the safety and usefulness of tubal recanalization. A meta-analysis of studies in patients undergoing FTR for bilateral tube blockage showed an 85–95% success rate in overcoming the obstruction, leading to a conception rate of 50%.
Is laparoscopy good for conceiving?
Will a laparoscopy hurt my chances of getting pregnant? For some women, who have undergone a laparoscopy to remove fibroids or endometriotic lesions, repair a hydrosalpinx, unblock a fallopian tube, or reverse a tubal ligation, the surgery actually increases the chances of getting pregnant.
What is the success rate of Recanalization surgery?
Interventional tubal recanalization or fallopian tube recanalization (FTR) is an extremely effective procedure for treating proximal tubal obstruction with a technical success rate as high as 90%.
Can a woman get pregnant after Recanalization?
This procedure successfully unblocks one or both tubes in up to 90% of patients. Intrauterine pregnancy after successful recanalization occurs in 30-50%, with most pregnancies occurring in the first three to six months after the procedure.
Is fallopian tube Recanalization painful?
There should be no lingering pain or other unpleasant sensation.
How successful is laparoscopy to unblock fallopian tubes?
The success rate of this method can be up to 85%; Laparoscopic surgery to remove adhesions of fallopian tubes and fallopian tubes: For cases where the fallopian tubes are attached due to inflammation, which can easily lead to ectopic pregnancy, the patient needs to undergo surgical dilation and removal of the fallopian ...
Is Recanalization good?
The proportion of patients with good general functioning was significantly higher among those with successful recanalization: 64.3% of patients with successful recanalization showed good general functioning at 24 weeks, compared to 42.9% of those without recanalization.
When is fallopian tube Recanalization?
A tubal recanalization procedure begins with an HSG. The patient should be scheduled usually within 5–11 days of her menstrual cycle in the follicular phase of her cycle prior to ovulation.
Can laparoscopic surgery unblock fallopian tubes?
Laparoscopic or hysteroscopic surgery to repair the Fallopian tubes. These minimally invasive procedures can repair blocked Fallopian tubes. A laparoscopy involves a small telescope being inserted through a small incision in the patient's belly button. The recovery time for this treatment is usually two to three days.
How quickly can Recanalization occur?
Studies have shown that early recanalization usually occurs between 2 and 6 weeks post-vasectomy.
What is the purpose of Recanalization?
This process facilitates clot lysis and continually improves residual flow until the clot breaks up under the pressure of arterial blood pulsations. Recanalization time may be an important clinical parameter of thrombolysis.
Can you get pregnant after laparoscopic tubal?
Tubal ligation is one of the most effective ways to prevent pregnancy, with rates of pregnancy around 1/1,000 after the first year, and between 2-10/1,000 after five years. Although the possibility of becoming pregnant is low, the chance is still there.
What is the recovery time for fallopian tube Recanalization?
If a blockage is identified, the doctor will attempt to open the blockage by inserting a small, soft catheter through the blockage. The entire procedure typically lasts only 30 minutes, patients go home the same day, and there is little to no recovery time needed.
What is the meaning of Wertheim?
Radical hysterectomy performed by way of an abdominal incision.
What is the Wertheim surgery procedure?
The principle of Wertheim's hysterectomy is to remove the uterus and the cervix with appropriate parametrium and tissues surrounding the upper vagina and pelvic lymph nodes.
Laparoscopic Wertheim’s surgery involves the removal of the Fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, ovaries as well as nearby lymph nodes and the upper portion of the vagina. The tissues removed depend upon the surgeon and the reason for surgery.
For example, if a woman has cancer of the uterus and if there is a suspicion that cancer has spread there then we remove the entire ovary. In other cases, if a woman who has chronic bleeding problems treated with only a portion of the uterus being removed. So this surgery includes removal of uterus, fallopian tube, lymph depending on the disease and surgeon who handles the case.
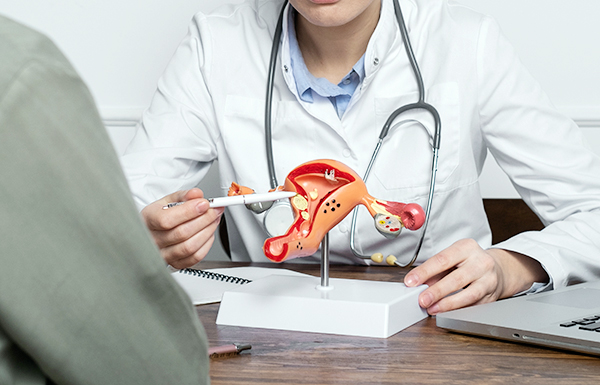
What is removed in a Wertheim's hysterectomy?
Wertheim's hysterectomy is to remove the uterus and the cervix with appropriate parametrium and tissues surrounding the upper vagina and pelvic lymph nodes.
What structures are cut in Wertheim hysterectomy?
Radical hysterectomy (Wertheim's hysterectomy) and pelvic lymphadenectomy for cervical cancer are intricate surgeries. The principle of Wertheim's hysterectomy is to remove the uterus and the cervix with adequate parametrium and vagina.
Why need to do laparoscopic Wertheim?
1) Fibroids: These tumors are not like cancer, but can cause pain, bleeding, cramping and discomfort.
2) Endometriosis: This is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus begins to spread to areas outside of the uterus, causing pain, cramping, miscarriage, infertility and chronic bleeding.
3) Cancer: Cancer of the uterus or other areas of the female reproductive system may require a hysterectomy as part of treatment.
4) Chronic Bleeding: Chronic bleeding can result from many different conditions that affect the uterus. Symptoms caused by chronic bleeding include anemia, weakness and chronic fatigue along with the worry and decrease in quality of life.
5) Chronic Pain: Unexplained chronic pelvic pain is often the reason for a hysterectomy, especially when pain changes into extreme and unbearable. When the source of the pain cannot be isolated or is difficult to treat. We perform surgery in this case.
Advantages
- The benefits of minimal invasive surgery are less wound-related problems.
- Increased patients comfort.
- Less blood loss.
- Short recovery time.
The Laparoscopic Transabdominal Cerclage (TAC) is a surgical procedure to treat cervical insufficiency. A suture is placed around the cervix at its uppermost part near the transition with the uterine body.
What is the success rate of a laparoscopic cervical cerclage?
It has a success rate of 79%–100%. The most common indication for LTAC in women with cervical incompetence is failed vaginal cerclage in prior pregnancies.
How long do you have to rest in bed after cervical cerclage?
You should plan to rest the day of your procedure and not attend school or work. Your healthcare provider will want you to allow plenty of time for your stitches to heal — about 10 days — before you engage in any strenuous exercise or sexual intercourse.
Is normal delivery possible after cervical cerclage?
Conclusion: The mean interval between elective cerclage removal and spontaneous delivery is 14 days. Women with cerclage who achieved 36-37 weeks should be counseled that their chance of spontaneous delivery within 48 hours after elective cerclage removal is only 11%.
When is the best time for cervical cerclage?
A cerclage is done in the second trimester of pregnancy to prevent preterm birth. Why is a cerclage placed? Sometimes the cervix isn't strong enough to stay closed as the pregnancy grows. This weakness is called cervical insufficiency (formerly called an incompetent cervix).
Can I climb stairs after cervical cerclage?
Family and friends may tell you to avoid climbing stairs after having a cervical stitch. However, there is no scientific evidence yet to prove that this could cause any issues. Each case is different, so consult your doctor for any advice.
Does bed rest help cerclage?
Conclusions Therapeutic cerclage with bed rest increases cervical length more often than bed rest alone. A postinter- vention cervical length ≥ 25 mm reduces the risk of preterm delivery in women at high risk of cervical incompetence and a preintervention cervical length < 25 mm.